Selection of the right type of machine in multi-axis CNC machining is among the most crucial decisions. It determines the overall capabilities of the process, the designs that are possible, and the overall costs. 3-axis vs 4-axis vs 5-axis CNC machining is a popular debate and the right answer depends on the requirements of the project.
This guide will take a look at the basics of multi-axis CNC machining and compare 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC machining to assist in making the right choice.
Introduction to 3-Axis Machining

The spindle moves around linearly in X, Y, and Z directions and the workpiece needs fixtures that hold it in one plane. The option to operate on multiple planes is possible in modern machines. But they require special fixtures that are slightly expensive to make and consume a lot of time as well.
There are, however, some limitations to what 3-axis CNCs can do as well. Many features are either economically unviable, despite the relative prices of 3-axis CNCs, or are simply impossible. For instance, 3-axis machines can’t create angled features or anything that’s on the X-Y-Z coordinate system.
Contrarily, 3-axis machines can create undercut features. However, they need several pre-requites and special cutters like T-slot and Dovetail cutters. Fulfilling these requirements can sometimes skyrocket the prices and sometimes it becomes more viable to opt for a 4-axis or 5-axis CNC milling solution.
Introduction to 4-Axis Machining
4-axis machining is more advanced than its 3-axis counterparts. In addition to the movement of the cutting tool in X-Y-Z planes, they allow the workpiece to rotate on the Z-axis as well. Doing so means that 4-axis milling can work on as many as 4 sides without any special requirements like unique fixtures or cutting tools.
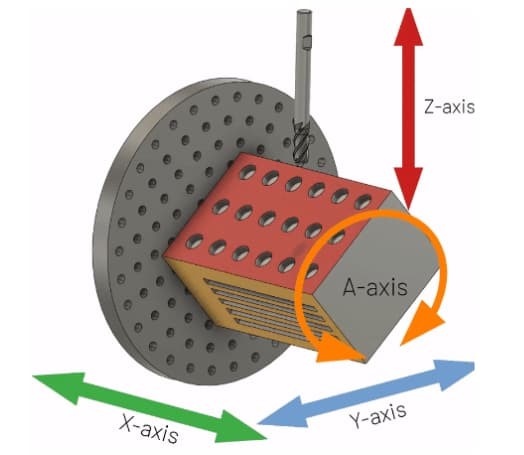
As stated before, the additional axis on these machines makes them more economically viable for some cases where 3-axis machines can get the job done, but with special requirements. The additional cost needed to make the right fixtures and cutting tools on 3-axis exceed the overall cost difference between the 4-axis and 3-axis machines. Thereby making them a more viable choice for some projects.
Moreover, another important aspect of 4-axis milling is the overall quality. Since these machines can work on 4 sides at once, repositioning the workpiece on the fixtures is not needed. Thereby minimizing the chances of human error and improving overall accuracy.
Today, there are two types of 4-axis CNC machining; continuous and indexing.
Continuous machining allows the cutting tool and the workpiece to move at the same time. This means that the machine can cut material while it’s rotating. Thereby making complex arcs and shapes like helixes very simple to machine.
Indexing machining, on the other hand, works in stages. The cutting tool stops once the workpiece starts to rotate around the Z-plane. This means that indexing machines don’t have the same capabilities because they can’t create complex arcs and shapes. The only benefit is the fact that the workpiece can now be machined on 4 different sides without needing any special fixtures that are essential in a 3-axis machine.
Introduction to 5-Axis Machining
5-axis machining takes things one step further and allows rotation on two planes. This multi-axis rotation along with the cutting tool’s ability to move in three directions are the two integral qualities that make it possible for these machines to handle the most complex jobs.
There are two kinds of 5-axis CNC machining available in the market. 3+2-axis machining and continuous 5-axis machining. Both operate in all planes but the former has the same limitations and working principle as an indexing 4-axis machine.
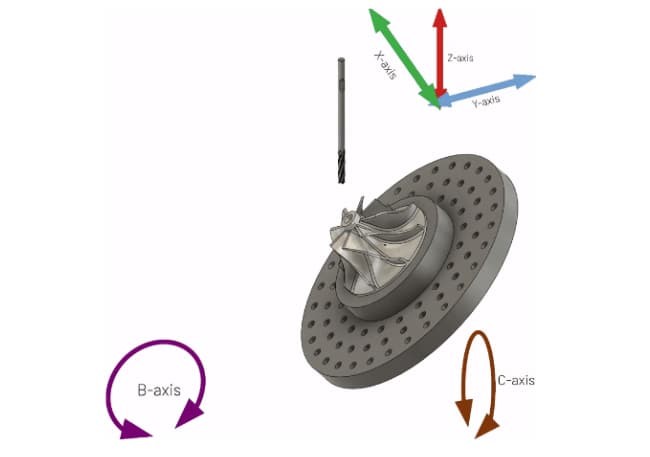
The 3+2 axis CNC machining allows rotation to be independent of each other but restricts the use of both coordinate planes at the same time. Contrarily, continuous 5-axis machining doesn’t come with such restrictions. Thereby allowing superior control and the ability to conveniently machine the most complex geometries.
Main Differences Between 3, 4, 5 Axis CNC Machining
Understanding the complexities and limitations of the kind of CNC machining is integral to ensuring the best balance between the cost, time, and quality of the process.
As stated before, numerous projects would be more expensive on an otherwise economical 3-axis milling because of the intricacies related to fixtures and processes. Similarly, simply opting for a 5-axis milling for every single project would be synonymous with combatting cockroaches with a machine gun. Doesn’t sound effective, right?
That is precisely the reason why it’s essential to understand the main differences between 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis machining. Doing so can ensure that the best kind of machine is selected for any particular project without any compromise on the essential quality parameters.
Here are the 5 main differences between the kinds of CNC machining.
Working Principle
The working principle of all CNC machining is the same. The cutting tool guided by a computer revolves around the workpiece to remove material. Furthermore, all CNC machines either use M-Codes or G-Codes to decipher the movement of the tool relative to the workpiece.

The difference comes in the additional capability to rotate about different planes. Both 4-axis and 5-axis CNC milling allow rotation about different coordinates and this quality results in the creation of more complex shapes with relative ease.
Precision & Accuracy
CNC machining is known for its accuracy and low tolerances. However, the type of CNC does affect the final tolerances of the product. 3-axis CNC, albeit very accurate, will have more chances of random errors due to consistent repositioning of the workpiece. For most applications, this margin of error is negligible. However, for sensitive applications pertaining to aerospace and automobile applications, even the smallest deviation can cause issues.

Both 4-axis and 5-axis CNC machining don’t have that issue as they don’t need any repositioning. They allow cutting on multiple planes on a single fixture. Furthermore, it’s important to note that this is the only source of discrepancy in the quality of 3-axis machining as well. Apart from this, the overall quality in terms of precision and accuracy remains the same.
Applications
Rather than industry-wide application, the differences in the type of CNC pertain to the nature of the product. For instance, the difference between 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling products will be based on the overall complexity of the design rather than the industry itself.

A simple part for the aerospace sector can be developed on a 3-axis machine while something complex for any other sector might require the use of a 4-axis or 5-axis machine.
Costs
Costs are among the primary differences between 3, 4, and 5-axis CNC milling. 3-axis machines are naturally more economical to purchase and maintain. However, the expenses of using them depend on factors like the fixtures and the availability of the operators. While the expenses incurred on operators remain the same in the case of 4-axis and 5-axis machines, the fixtures still take up a significant portion of the expenses.
On the other hand, 4 and 5-axis machining are more technologically advanced and have better features. Therefore, they are naturally expensive. However, they bring a lot of capabilities to the table and are a viable choice in many unique cases. One of them has already been discussed before where a design theoretically possible with a 3-axis machine would need a lot of custom fixtures. Thereby increasing the overall costs and making 4-axis or 5-axis machining a more viable option.
Lead Time
When it comes to the overall lead times, continuous 5-axis machines provide the best overall results. They can process even the most complex shapes in the shortest time because of a lack of stoppages and single-step machining.
Continuous 4-axis machines come after that as they allow rotation in one axis and can only handle planar angular features in one go.
Finally, 3-axis CNC machines have the longest lead time because the cutting takes place in stages. Furthermore, the limitations of 3-axis machines mean that there will be a lot of repositioning of the workpiece, which would result in an increase in the overall lead times for any project.
3 Axis vs 4 Axis vs 5 Axis Milling, Which Is Better?
In manufacturing, there is no such thing as an absolutely better method or a one-size-fits-all solution. The right choice depends on the intricacies of the project, the overall budget, time, and the quality requirements.
3-axis vs 4-axis vs 5-axis, all have their merits and demerits. Naturally, the 5-axis can create more complex 3D geometries, while 3-axis can quickly and consistently churn out simpler pieces.
To sum up, there is no answer to the question of which one is the better choice. Any machining method that delivers the perfect balance between cost, time, and results would be an ideal choice for a particular project.
Read more: CNC Milling vs CNC Turning: Which Is Right to Choose
Start Your Projects with Guansheng’s CNC Machining Services
For any project or business, the right manufacturing partner can be the difference between success and failure. Manufacturing is an integral part of the product development process and the right choices in that stage can go a long way toward making a product viable. Guangsheng is the ideal manufacturing choice for any situation because of its insistence on delivering the best with the utmost consistency.
Equipped with a state-of-the-art facility and experienced team, Guangsheng can handle all kinds of 3-axis, 4-axis, or 5-axis machining jobs. With stringent quality checks in place, we can guarantee final parts meet all kinds of quality checks without fail.
Furthermore, what sets Guangsheng apart is its fastest lead times and the most competitive prices in the market. Moreover, the process is also optimized to facilitate the customer. Simply upload the designs to get a comprehensive DFM analysis and an instant quote to get started.
Automation and online solutions are the keys to the future of manufacturing and Guangsheng understands that. That is why everything you’ll need for the best results is only a click away.
Conclusion
All 3, 4, and 5-axis CNCs are different and each type comes with its strength or weaknesses. The right choice, however, comes down to the unique requirements of a project and its demands. There is no right choice in manufacturing. The correct approach is to find the most optimum combination of quality, cost, and time. Something all three types of CNC can deliver based on the requirements of a particular project.
Post time: Nov-29-2023
